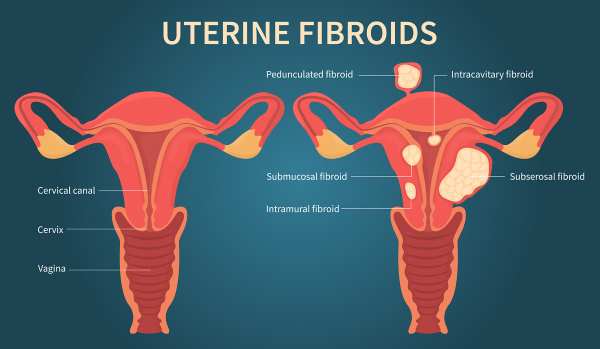
Uterine fibroids (UFs) represent the most prevalent non-cancerous tumors among women of reproductive age. Symptomatic fibroids can lead to significant health issues and are the primary reason for hysterectomies in the United States and globally, contributing to substantial socioeconomic impacts and affecting over 70% of women of reproductive age (Langton et al., 2024). African American women tend to develop fibroids approximately 10 years earlier than White women in the US and bear a disproportionate health burden from these tumors
Black women experience UFs at higher rates, with an earlier onset, more severe symptoms, and faster disease progression compared to other groups.
According to Sithembinkosi Ndebele (2024), 85% of participants were non-Hispanic Blacks. Black participants had a higher likelihood of a UF diagnosis, and the following risk factors were reported contributing to the high prevalence of UFs in Black individuals:
- Socioeconomic Status: Lower socioeconomic status is reported to increase the rates of UFs.
- Adverse Environmental Exposures: Increased exposure to environmental pollutants is associated with a higher prevalence of UFs.
- Chronic Stress: Experiences that increase chronic stress are significant contributors.
Lifestyle and socioeconomic factors, closely tied to neighborhood characteristics, further influence UF prevalence. These factors include:
- Body Mass Index (BMI): A higher BMI correlates with a higher risk of UFs.
- Alcohol Use: Regular alcohol consumption is positively correlated with UF diagnosis.
- Income and Occupation: These factors influence access to healthy food and healthcare.
 The four-stage process to regain control of Postpartum Depression
The four-stage process to regain control of Postpartum DepressionPostpartum depression (PPD) is characterized by a major depressive episode that begins within four to six weeks following delivery, as per international diagnostic criteria. Recurrence rates for PPD are high, with 40% of affected women experiencing depression again in their lifetime and nearly 50% facing another episode in subsequent pregnancies. Symptoms of PPD encompass fatigue, irritability, anxiety, lack of pleasure, feelings of helplessness, sleep and appetite disturbances, indifference towards life events, low self-esteem, and feelings of incompetence as a parent, among others. PPD is considered a multifactorial condition influenced by both environmental and genetic risk factors for depression.
Risk factors for PPD include:
- Previous depression.
- Adverse life events.
- Lack of social support.
- Socioeconomic position.
- Personal and family psychiatry history.
- Stressful experiences (such as trauma).
- Specific pregnancy-related factors.
- Intimate partner violence (IPV) occurring close to or during pregnancy also elevates the risk of postpartum depression.
The impacts of PPD are significant and extend beyond the affected individual. They include poor attachment between the mother and newborn, potential stunted growth and low weight in the child, disrupted breastfeeding, and adverse effects on the infant’s cognitive, emotional, and social development. There is also an increased risk for psychiatric disorders in the child during infancy, childhood, adolescence, and adulthood. Women of color and those with lower incomes are more likely to suffer from postpartum depression and may face barriers to accessing treatment (Gopalan et al., 202).
The four-stage process to regain control of Postpartum Depression
Women experiencing PPD often undergo a four-stage process in an attempt to regain control:
- In the initial stage, mothers grapple with intense worries, persistent obsessive thoughts, and difficulties focusing.
- In the second stage, women feel a sense of loss of their “regular selves,” describing a robotic feeling while caring for their infants. Withdrawal may occur, and thoughts of self-harm or suicide may surface.
- The third stage involves women planning strategies to overcome PPD, such as seeking help from healthcare providers, engaging in prayer, or finding comfort in support groups.
- In the final stage, women regain control of their thoughts and feelings as despair lifts.
 Contributing factors to the High Obesity Rates Among African American Women
Contributing factors to the High Obesity Rates Among African American WomenResearch reports that American women are disproportionately affected, with the highest obesity rates among all groups in the U.S. About 80% are classified as overweight or obese.
Disparities in weight loss
Research indicates that African American (AA) women tend to lose less weight compared to their Caucasian counterparts.
Contributing Factors
The contributing factors to the disparities are;
- Limited access to nutritious food
- Inadequate health insurance
- Lack of safe spaces for physical activity
Barriers to Weight Management
Challenges that hinder weight management efforts include:
- Personal beliefs
- Limited time
- Family dynamics
- Lack of motivation
- Financial constraints
Cultural Influence on Body Image
Cultural norms within the AA community, which often embrace larger body sizes and promote a positive body image, can also influence health behaviors. While fostering a positive body image has psychological benefits, it may reduce motivation to maintain a healthy weight. In Black culture, obesity and being overweight are often considered acceptable and carry little to no stigma. Cultural perspective may partially explain why general health promotion efforts are less effective in this community. The study reports that many Black female students aim to embody the culturally valued “thick and curvy” figure, consuming specific foods to shape their bodies while avoiding activities that might result in weight loss.
Why it may be difficult to seek care
A deep-rooted distrust of the healthcare system makes it difficult for many AA women to seek medical advice or treatment.
Physical inactivity as a health risk factor
Underestimating body weight can reduce engagement in healthy behaviors, such as regular physical activity. Physical inactivity is a major contributor to non-communicable diseases and mortality, emphasizing the need to address these issues within the AA community.
 Four Major Diseases linked to smoking
Four Major Diseases linked to smokingAccording to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2021), Cigarette smoking damages almost every organ in the body, leading to numerous diseases and overall health decline. In the United States, smoking is responsible for over 480,000 deaths each year, nearly one in five deaths. For women, smoking can make it more difficult to conceive and can adversely affect a baby’s health before and after birth. In men, smoking can reduce sperm quality, decreasing fertility and increasing the risk of congenital disabilities and miscarriage. Smoking also harms oral health, potentially leading to tooth loss. Moreover, it increases the risk of cataracts, which cloud the eye’s lens and impair vision. It can cause age-related macular degeneration (AMD), damaging a small spot near the retina’s center needed for central vision. Additionally, smoking is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes mellitus and can complicate its management, with active smokers having a 30-40% higher risk of developing diabetes compared to nonsmokers.
The four major diseases linked to smoking are
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Increased mortality rates due to smoking.
- Elevated risk of ischemic heart diseases.
- Respiratory Conditions
- Smoking is a primary cause of chronic respiratory deaths.
- Increased risk of respiratory diseases and tuberculosis.
- Stroke
- A Study reports a Positive correlation between smoking prevalence and stroke-related deaths.
- Lung Cancer
- Study reports there is a higher likelihood of lung cancer with increased daily cigarette consumption.
 Six Healthy Lifestyle Practices to Alleviate Depression Symptoms
Six Healthy Lifestyle Practices to Alleviate Depression SymptomsCauses of Depression
Depression can arise from a multitude of factors, such as genetic, environmental, psychological, and biochemical ones.
Risk factors for depression
A person is more likely to experience depression if they have trauma, significant life changes, stress, a family history of depression, physical illnesses (like diabetes, cancer, or Parkinson’s disease), or as a side effect of certain medications.
Diagnosis of major depression disorder
A minimum of two weeks must pass with some of these symptoms and signs being presented almost daily to be diagnosed with Major Depressive Disorder:
Common symptoms of depression
The common symptoms of depression include.
- Persistent sadness,
- Hopelessness,
- Pessimism,
- Emptiness,
- Lack of energy,
- Feeling guilty or unworthy. The lack of interest or pleasure in pastimes,
- Alterations in appetite that result in either weight gain or loss,
- Slower speech, movement, or thought.
- Increased fidgeting
- Difficulty focusing, thinking coherently, or making decisions
- Suicidal thoughts, suicidal attempts, thoughts of death, or self-harming behavior
Lifestyle Practices to Alleviate Depression Symptoms
- Self-care. Practice stress-reduction techniques like tai chi or meditation. Get enough sleep, exercise, and eat a balanced diet. For the most part, adults require 7 to 9 hours of sleep. Refrain from using recreational drugs and alcohol, as these can exacerbate symptoms and complicate the treatment of depression.
- Educating family and friends about depression: They can assist you in identifying early indicators that your depression might be relapsing.
- Maintain your treatment regimen. Continue taking your medication and attending therapy sessions even after you feel better. Sudden medication discontinuation may result in withdrawal symptoms and a relapse of depression. If necessary, work with your physician to modify your medication or dosage to adhere to your treatment plan.
- Make modest, achievable goals: realistic goals to increase motivation and self-assurance. During the first stages of care, you might want to walk, have lunch with a friend, or make a bed. Gradually increase your goals as you get better.
- Identify the warning signs: Determine what triggers your depression, and if you notice any unusual changes in your feelings, thoughts, or behavior, speak with your doctor or a mental health professional. Keep a journal of your daily emotions, feelings, and reactions to identify trends and identify the things that lead to depression.
- Seek support. Maintaining relationships with people is crucial, especially during difficult times or periods, regardless of whether you receive support from family or a support group.
 The Health Effects of Stress
The Health Effects of StressOverview of Stress: Stress significantly affects health, contributing to disease development and burdening healthcare systems considerably. It is a significant factor in various ongoing health issues, particularly cardiovascular diseases, which are often impaired by everyday psychosocial pressures, such as work-related stress.
The following are the roles of stress in disease development.
Gender Differences in Stress Responses: Gender plays a vital role in how individuals experience and manage stress. Research reports that women are more likely to develop mood disorders and autoimmune. At the same time, men tend to have higher rates of early substance abuse, infectious disease, mortality, and antisocial behavior. Unsuccessful stress management can lead to severe physical and mental health consequences for both individuals and communities.
Physiological Responses to Stress: The study reports that stressful events can trigger emotional responses such as anxiety and worry, impacting the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the sympathetic-adrenal-medullary (SAM) system, which may lead to unhealthy lifestyle choices, comprising poor sleep, alcohol consumption, decreased physical activity and increased smoking thereby increase the risk of diseases.
Chronic Stress in Specific Environments: Chronic stress in educational settings and workplaces impacts mental and physical health noticeably. Also, it indicates that occupational stress significantly affects mental well-being.
Traumatic Events as a Stress Source: Traumatic events are a prevalent source of stress that affects a large portion of the population. The study reports that In North America, about 60% to 75% of individuals will experience a traumatic event in their lifetime, including serious accidents, exposure to war, sexual assault, chronic childhood abuse, or neglect.
 Four lifestyle changes to reduce the development of Uterine Fibroids (UFs)
Four lifestyle changes to reduce the development of Uterine Fibroids (UFs)Uterine fibroids (UFs) are the most common benign tumors found in women of reproductive age, with a disproportionate impact on women of color. These disparities are believed to be combined with environmental, genetic, and socio-economic factors.
Some of the lifestyle changes that can help prevent or reduce the development of uterine fibroids are;
- Decreasing Alcohol consumption: It’s advised that women decrease their alcohol consumption to reduce the risk of developing uterine fibroids (UFs). Studies have reported an association between alcohol intake and an increased likelihood of UFs. Studies believe that alcohol may alter hormone levels and disrupt hormonal balance, contributing to the formation of UFs. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice based on unique health occurrences. By being mindful of alcohol consumption and adhering to recommended limits, proactive steps can be taken to lower the risk of UFs.
- Engage in at least four hours of vigorous physical activity per week: Research has found a significant association between an increased BMI and the risk of UFs. Obesity is believed to be a contributing factor to UF. Studies believe that women who engage in at least four hours of vigorous physical activity per week are more likely to encounter a decrease in the risk factors of UFs.
- Consuming more fruits, Vegetables, and dietary fibers: High intake of processed and refined foods, unhealthy fats, and sugary drinks, and low consumption of fruits, vegetables, and fiber-rich foods may contribute to hormonal imbalances, inflammation and oxidative stress, thereby encouraging the growth of UFs as indicated in the research. Additionally, a lack of fruits, vegetables, and fiber-rich foods has been reported to be associated with an elevated risk of UFs. Fruits, vegetables, and fiber-rich food are excellent sources of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that help combat oxidative stress and inflammation. Specifically, Dietary fiber has been indicated to have protective impacts against UFs by supporting hormonal balance and improving regular bowel movements. Hence, adopting a healthy and balanced diet with whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential.
- Managing stress: Studies have found that chronic psychological stress could increase the risk of uterine fibroids and indicated a significant link between chronic psychological stress and an elevated risk of UFs, predominantly among non-Hispanic Black women. Eating healthy, exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, relaxing, connecting with friends and family, and practicing mindfulness are some ways to manage stress.