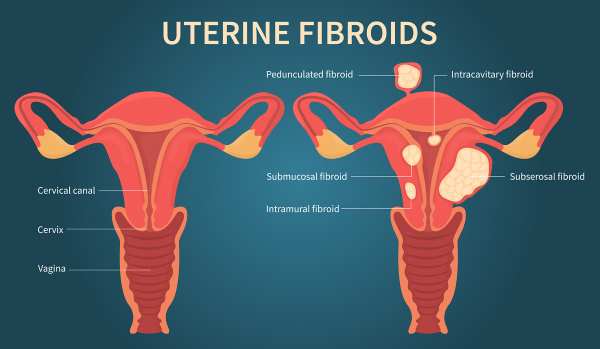
Uterine fibroids (UFs) represent the most prevalent non-cancerous tumors among women of reproductive age. Symptomatic fibroids can lead to significant health issues and are the primary reason for hysterectomies in the United States and globally, contributing to substantial socioeconomic impacts and affecting over 70% of women of reproductive age (Langton et al., 2024). African American women tend to develop fibroids approximately 10 years earlier than White women in the US and bear a disproportionate health burden from these tumors
Black women experience UFs at higher rates, with an earlier onset, more severe symptoms, and faster disease progression compared to other groups.
According to Sithembinkosi Ndebele (2024), 85% of participants were non-Hispanic Blacks. Black participants had a higher likelihood of a UF diagnosis, and the following risk factors were reported contributing to the high prevalence of UFs in Black individuals:
- Socioeconomic Status: Lower socioeconomic status is reported to increase the rates of UFs.
- Adverse Environmental Exposures: Increased exposure to environmental pollutants is associated with a higher prevalence of UFs.
- Chronic Stress: Experiences that increase chronic stress are significant contributors.
Lifestyle and socioeconomic factors, closely tied to neighborhood characteristics, further influence UF prevalence. These factors include:
- Body Mass Index (BMI): A higher BMI correlates with a higher risk of UFs.
- Alcohol Use: Regular alcohol consumption is positively correlated with UF diagnosis.
- Income and Occupation: These factors influence access to healthy food and healthcare.
 How to Survive During Rising Costs and Government Shutdown
How to Survive During Rising Costs and Government ShutdownWith the government shutdown, many aspects of daily life have been severely impacted. The rate of food insecurity is increasing, and challenges related to housing, transportation, and other social determinants of health are becoming more pressing. SNAP benefits have been frozen, leaving many families struggling to put food on the table. As a result, more individuals and families are turning to food pantries and community resources for support.
At the same time, the cost of food and necessities continues to rise, deepening the struggles faced by countless households. These are difficult times, but I want to encourage everyone affected to stay strong, remain hopeful, and trust that better days are ahead.
Here are some practical ways to cope and survive during the rising costs and government shutdown:
Prioritize Your Needs
- You must focus on needs such as housing, food, transportation, utilities, and medication.
- Decrease or pause non-essential spending, such as new purchases, entertainment, or dining out.
Manage Your Money Wisely
- Avoid any unnecessary debt.
- Prioritize rent/mortgage and food.
- Discuss with your utility company, landlord, or bank to explore any available payment plans or deferments during the shutdown.
Explore any available community resources
- Assess community and faith-based resources (Local food banks, churches, non-profits) for support with food and bills.
- Check your city’s website to find out what supports are available to access.
Protect Your Mental and Emotional Health during the difficult time
- Financial insecurity can be draining. Stay connected with family, friends, and coworkers for emotional support.
- Get good exercise, rest, and be consistent with your routines
- Have faith and be hopeful that the challenges are temporary and will surely pass
- Focus on what’s within your control.
Maintain Perspective
- Use this period to build your financial discipline and strength
- Celebrate each time you pay a bill and make meals; a win is worth celebrating
- Reflect on value by focusing on more relationships, essentials, and faith than on any material things
 Six Healthy Lifestyle Practices to Alleviate Depression Symptoms
Six Healthy Lifestyle Practices to Alleviate Depression SymptomsCauses of Depression
Depression can arise from a multitude of factors, such as genetic, environmental, psychological, and biochemical ones.
Risk factors for depression
A person is more likely to experience depression if they have trauma, significant life changes, stress, a family history of depression, physical illnesses (like diabetes, cancer, or Parkinson’s disease), or as a side effect of certain medications.
Diagnosis of major depression disorder
A minimum of two weeks must pass with some of these symptoms and signs being presented almost daily to be diagnosed with Major Depressive Disorder:
Common symptoms of depression
The common symptoms of depression include.
- Persistent sadness,
- Hopelessness,
- Pessimism,
- Emptiness,
- Lack of energy,
- Feeling guilty or unworthy. The lack of interest or pleasure in pastimes,
- Alterations in appetite that result in either weight gain or loss,
- Slower speech, movement, or thought.
- Increased fidgeting
- Difficulty focusing, thinking coherently, or making decisions
- Suicidal thoughts, suicidal attempts, thoughts of death, or self-harming behavior
Lifestyle Practices to Alleviate Depression Symptoms
- Self-care. Practice stress-reduction techniques like tai chi or meditation. Get enough sleep, exercise, and eat a balanced diet. For the most part, adults require 7 to 9 hours of sleep. Refrain from using recreational drugs and alcohol, as these can exacerbate symptoms and complicate the treatment of depression.
- Educating family and friends about depression: They can assist you in identifying early indicators that your depression might be relapsing.
- Maintain your treatment regimen. Continue taking your medication and attending therapy sessions even after you feel better. Sudden medication discontinuation may result in withdrawal symptoms and a relapse of depression. If necessary, work with your physician to modify your medication or dosage to adhere to your treatment plan.
- Make modest, achievable goals: realistic goals to increase motivation and self-assurance. During the first stages of care, you might want to walk, have lunch with a friend, or make a bed. Gradually increase your goals as you get better.
- Identify the warning signs: Determine what triggers your depression, and if you notice any unusual changes in your feelings, thoughts, or behavior, speak with your doctor or a mental health professional. Keep a journal of your daily emotions, feelings, and reactions to identify trends and identify the things that lead to depression.
- Seek support. Maintaining relationships with people is crucial, especially during difficult times or periods, regardless of whether you receive support from family or a support group.
 The Struggle to Survive: Living Through the Rising Cost
The Struggle to Survive: Living Through the Rising CostThe rising cost of living has become a significant public health concern, particularly for low-income individuals who are struggling daily to survive. Addressing the social determinants of health among this population remains an urgent issue, as many face ongoing challenges accessing essential needs such as food, housing, transportation, and healthcare. During my assessment of some of the low-income individuals, I found that several individuals eat only once a day to save money for rent. Many reported choosing to go hungry rather than risk homelessness. Some have been living in their cars for nearly a year, while others rely on the homes of friends to shower and change clothes. It is heartbreaking to witness the difficult situations people endure every day to stay alive.
The rising cost of living has multiple impacts on health and well-being. According to Grewal et al. (2024), increasing housing costs—one of the key components of living expenses—can have both direct and indirect health consequences. Their study indicates that:
- Financial strain from high housing and living expenses contributes to increased stress, anxiety, and depression, particularly among renters and low-income individuals.
- Food insecurity often results when households must prioritize rent or transportation over nutrition, leading to poor dietary intake and higher risks of chronic diseases.
- Limited access to healthcare arises when individuals cannot afford medical visits, medications, or preventive care due to competing financial demands.
- Housing instability or homelessness can expose individuals to unsafe environments, lack of sanitation, and interrupted social support networks, which worsen both physical and mental health outcomes.
Overall, Grewal et al. (2024) emphasize that the effects of rising housing and living costs are unequally distributed, disproportionately affecting low-income individuals who already face multiple barriers to health. This highlights the need for comprehensive policy approaches that integrate housing affordability, income support, and healthcare access as essential strategies to promote health equity.
Source: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18360-w
 The Health Effects of Stress
The Health Effects of StressOverview of Stress: Stress significantly affects health, contributing to disease development and burdening healthcare systems considerably. It is a significant factor in various ongoing health issues, particularly cardiovascular diseases, which are often impaired by everyday psychosocial pressures, such as work-related stress.
The following are the roles of stress in disease development.
Gender Differences in Stress Responses: Gender plays a vital role in how individuals experience and manage stress. Research reports that women are more likely to develop mood disorders and autoimmune. At the same time, men tend to have higher rates of early substance abuse, infectious disease, mortality, and antisocial behavior. Unsuccessful stress management can lead to severe physical and mental health consequences for both individuals and communities.
Physiological Responses to Stress: The study reports that stressful events can trigger emotional responses such as anxiety and worry, impacting the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the sympathetic-adrenal-medullary (SAM) system, which may lead to unhealthy lifestyle choices, comprising poor sleep, alcohol consumption, decreased physical activity and increased smoking thereby increase the risk of diseases.
Chronic Stress in Specific Environments: Chronic stress in educational settings and workplaces impacts mental and physical health noticeably. Also, it indicates that occupational stress significantly affects mental well-being.
Traumatic Events as a Stress Source: Traumatic events are a prevalent source of stress that affects a large portion of the population. The study reports that In North America, about 60% to 75% of individuals will experience a traumatic event in their lifetime, including serious accidents, exposure to war, sexual assault, chronic childhood abuse, or neglect.
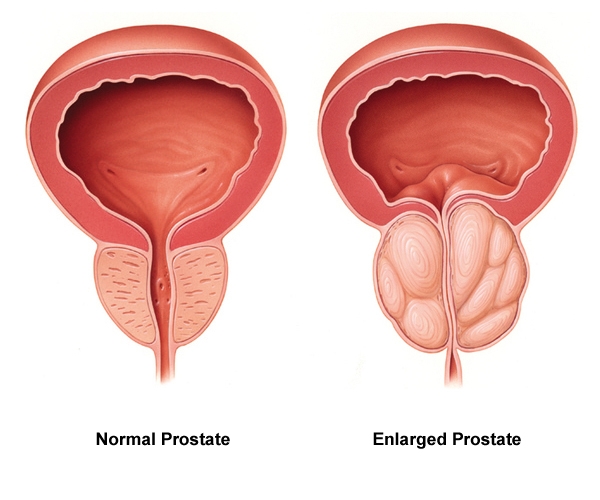 Male Health and Prostate Diseases
Male Health and Prostate DiseasesThe prostate is a small, walnut-sized, shaped organ below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The main functions are to create fluids for semen and force semen through the urethra during ejaculation. It is usual for the prostate to get larger as one age. Because of the location just below the bladder and in front of the rectum, also wrapping around the upper part of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body, it means abnormal prostate conditions can affect urination and sexual function. The prostate is prone to three main conditions, which are Prostatitis, an infection or inflammation of the prostate gland; Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), an aging-related enlargement of the prostate gland; Prostate cancer, the growth of cancerous cells inside the prostate, which may break out of the gland and affect other parts of the body.
Prostatitis
This is the inflammation (swelling) of the prostate gland, and common causes include infection (usually bacteria), injury, or an immune system disorder. The symptoms may include the inability to urinate, Painful or difficult urination, and painful ejaculation, accompanied by fever, Blood in the urine (hematuria), and Severe discomfort or pain in the pelvic area or genitals.
The Risk factors for prostatitis include:
Previous prostatitis, Infection of the urinary or reproductive system, HIV infection or AIDS, Use of a tube inserted into the urethra to drain the bladder (urinary catheter), and Diagnostic sampling of prostate tissue (biopsy).
Laboratory tests for Prostatitis include Urinalysis, urine microscopy/culture/sensitivity, HIV, measurement of Prostatic specific antigen levels in the blood, Scan, etc.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
The prostate will almost certainly get larger increasing age. A small amount of prostate enlargement is present in many men over age 40 years of age. More than 90% of men over age 80 have the condition. It’s not clear why it happens, but it may be linked to the decline in the male sex hormone testosterone with aging. This enlargement is a condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). The key word is benign. BPH has nothing to do with cancer and doesn’t increase the risk of prostate cancer. It can make urination and ejaculation difficult because as the prostate grows, it presses on the urethra. That interferes with the flow of urine and the release of ejaculate during orgasm. In less than half of all men with BPH, symptoms may include dribbling at the end of urinating, Inability to urinate (urinary retention), Incomplete emptying of the bladder, Incontinence, needing to urinate two or more times per night, Pain with urination or bloody urine (these may indicate infection). Slowed or delayed the start of the urinary stream, straining to urinate, Strong and sudden urge to urinate, and Weak urine stream.
The Link between BPH and Sexual Problems
Scientists aren’t sure why, but they agree that the worse the BPH symptoms are, the more likely an individual is to have sexual issues such as reduced sex drive, trouble keeping an erection, and less sexual satisfaction. It may have something to do with genetics or age. It’s also possible that the sleeplessness or anxiety that can come from an enlarged prostate makes sexual problems worse.
Laboratory Test for BPH.
A digital rectal exam is usually done to feel the prostate gland. Urine flow rate is monitored, Urinalysis to check for blood or infection, Urine culture to check for infection, Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test to screen for prostate cancer, Cystoscopy, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine tests to check for reduced kidney function.
Risk Factors for BPH include;
- Age – symptoms start manifesting by age 50 to 60 in 60% of men.
- Unhealthy diet- daily consumption of a diet high in red or processed meat, saturated fats, and dairy products can increase your risk for prostate problems. Sodium (salt), Alcoholic and caffeinated beverages like coffee, tea, and soda can also increase your risk due to being diuretics that increase urine production.
- Type 2 diabetes, poorly managed Hypertension, and other heart diseases, Smoking, obesity, and a Sedentary lifestyle are common risk factors.
- Prostatitis
- Family history/genetics
- Frequent Urinary Tract infection (UTI)
Prostate Cancer
Cancer is a disease in which abnormal cells divide uncontrollably and destroy body tissue, in the case of prostate, abnormal prostate cells continue to grow until it has destroyed normal body tissues around and beyond the prostate. Prostate cancer usually develops slowly, so there may be no signs for many years. Symptoms of prostate cancer do not usually appear until the prostate is large enough to affect the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the penis (urethra). When this happens, one may notice things like increased need to pee, straining while peeing, a feeling that the bladder has not fully emptied. Causes of prostate cancer are largely unknown. However, certain things can increase the risk of developing the condition.
Risk factors for Prostate cancer include;
- Age: The chances of developing prostate cancer increase as one gets older. Most cases develop in men aged 50 or older. Prostate cancer risk begins to rise sharply after age 55 years and peaks at age 70–74, after which it starts to decline. For reasons not yet understood, prostate cancer is more common in black men and less common in Asian men.
- Men whose fathers or brothers were affected by prostate cancer are at slightly increased risk themselves.
- Other risk factors include Obesity, Smoking (increases steroid hormone production such as DHT, and estrogen), High levels of pesticides, excessive consumption of dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese, lactose-free milk, and fortified soy milk and yogurt), excessive red meat consumption, Saturated fat, and Sedentary lifestyle.
Beneficial Foods to Eat
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, such as the Mediterranean diet, may benefit health. Salmon, rich in healthy fats that contain omega-3 fatty acids, helps prevent and reduce inflammation within the body, and other cold-water fish, such as sardines and trout, are also rich in these fats.
Tomatoes: Tomatoes are packed with lycopene, an antioxidant that may benefit prostate gland cells. Cooking tomatoes, such as in tomato sauce or soup, helps to release the lycopene and make it more readily available to the body. Berries: Strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries are excellent sources of antioxidants, which help to remove free radicals from the body. Free radicals are the byproducts of reactions that occur within the body and can cause damage and disease such as concern over time.
Broccoli: Broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables, including bok choy, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage, contain a chemical known as sulforaphane. This is thought to target cancer cells and promote a healthy prostate.
Nuts: Nuts are rich in zinc, a trace mineral. Zinc is found in high concentrations in the prostate and is thought to help balance testosterone and DHT. Besides nuts, shellfish and legumes are also high in zinc.
Citrus: Oranges, lemons, limes, and grapefruits are all high in vitamin C, which may help to protect the prostate gland.
All these are vital in addition to exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, such as brisk walking, Kegel exercise, and moderate strength training.
(Written by Ebenezer Dic-Ijiewere PhD.)
 Should we throw away our medicines after the ‘Best Before’ or Expiry date?
Should we throw away our medicines after the ‘Best Before’ or Expiry date?Introduction
One of man’s best inventions is drugs, especially disease-specific ones. Drugs are substances other than food, which can prevent, relieve the symptoms, or cure an abnormality or disease. Globally, the cost of drugs has soared over the years, resulting in a situation whereby low-income earners are unable to buy branded medications. In underdeveloped and developing countries where food and drug agencies have poor capacity to perform their regulatory functions optimally, we tend to see the proliferation of substandard or fake drugs. So many times, this ugly trend is energized by not just greed but by the market demands for affordable medications.
Why Medication exceeds expiry date
To mitigate the challenge of not being able to buy drugs, when necessary, people from resource-limited settings stack up some essential medications in their homes, which eventually exceed the best before or expiry dates on them. Sometimes, doctors could change a patient’s prescription because of reactions, allergies, or inability to purchase the drug, which could result in leftover drugs that eventually exceed the expiration date. Also, big pharmacies and patent-drug stores cannot sell all their stock, leading to the expiration of some drugs. This situation has raised many questions about the safety of these drugs after their expiration or beyond the “best before” date. Because of the importance of drugs and the health risks involved when taken wrongly, people have always consciously discarded unused drugs when it’s past the expiration date, even one day.
How Safe is a drug after the expiry date?
The debate about drugs being safe after their expiration date has persisted over the years, as many people still hold the opinion that pharmaceutical companies deliberately label their drugs with short shelf lives to guarantee steady patronage. Eventually, most of these unused drugs are discarded. The context that drugs can still be safe for a long time after expiration has gained several affirmations. In a recent study by Benjamin Davido and others titled ‘Efficacy of Expired Antibiotics: A Real Debate in the Context of Repeated Drug Shortages’ published in MDPI Journal “Antibiotics”, it was reported that when appropriately stored in line with the expected conditions, no expired antibiotics tested failed to be potent after one year of expiration. In another study by Sushil Sharma and others, titled ‘A study to investigate the chemical potency, physical stability, and efficacy of analgesic agents over a period of two years post their expiry date’ published in the “Medical Journal Armed Forces India”, it was seen that drugs such as Diclofenac, Piroxicam, and Ibuprofen retained their stability, analgesic efficacy, chemical active ingredients and by implication their potency up to a duration of two years after expiration.
Important factors to consider
However, the issues of proper storage and handling can play a big role, especially in the tropical climate of West Africa and other geographical regions. Hence, people in the tropics may have to rely on their capacity to store their drugs in the required condition in deciding whether to use a drug past the expiration date or not.
Conclusion
This article doesn’t advocate for the use of expired medication but to reduce anxiety about accidental use. It is essential to understand factors that impact drug stability.
(Written by Ebenezer Dic-Ijiewere PhD.)
NB: Always consult your healthcare professionals regarding expired medications to ensure medication safety and effectiveness.